How are rough diamonds cut into different shapes? Everything Explained
Posted by Hari Krishna
December 7, 2022
All of us know how diamonds are formed – deep within the Earth’s surface, over millions of years and under great pressure. But those are actually rough diamonds and do not look anything like the sparkling pieces we know diamonds to be.
So how does it go from rough to polished? What effect does it have on the value, price and beauty of the diamond? How can I get my hands on the most beautifully cut diamonds?
This blog will detail the process of diamond manufacturing and will be your full guide for diamond cutting.
Your key takeaways will be
Probably the most important step is the planning of a rough diamond. Since the rest of the steps actually just execute whatever was decided in this step. If a mistake is made here, it is already a lost cause because planning determines;
Firstly, one needs to carefully examine the rough diamond manually and with the help of a software, and to do it precisely, it should be done by the experienced and skilled diamond cutter.
The cutter considers and analyzes all the possibilities before finalizing the best possible shape of the diamond to minimize the waste and maximize its final quality and value.
After analyzing its size, shape, clarity, and crystal direction and finalizing its shape the second thing to plan is the proportioning of facets and quality of the cut (i.e. symmetry & polish). This step is generally done through computer simulations.
Normally, ‘Sarin Machine’ is used to generate accurate measurements and formulate 3D models that will show the best ways to optimize the rough stone.
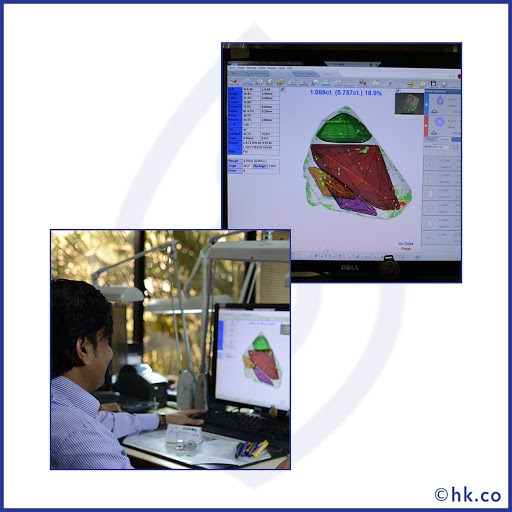
This process requires expertise in diamond cutting, as it is the cut that determines the diamond’s possibility to reflect light which ultimately affects its end-value.
Once the diamond is planned, and it is determined what shape and size is best for the rough diamond, it is then marked.
Just like the name suggests it is the “marking” done on a diamond which shows where and how the cuts are to be made.
Diamond marking is done by examining and measuring the dimensions of the rough stone under a magnifying glass.
This step is a decisive process in deciding the ultimate value of your finished diamond based on how much percentage of the weight and color of the original rough stone is retained in the finished diamond.
Any flaws in the marking of the diamond even small as thread cause a significant change in the clarity grade of the final diamond. So it is better to cut a few small stones of higher clarity grade than one large stone of lower clarity grade.
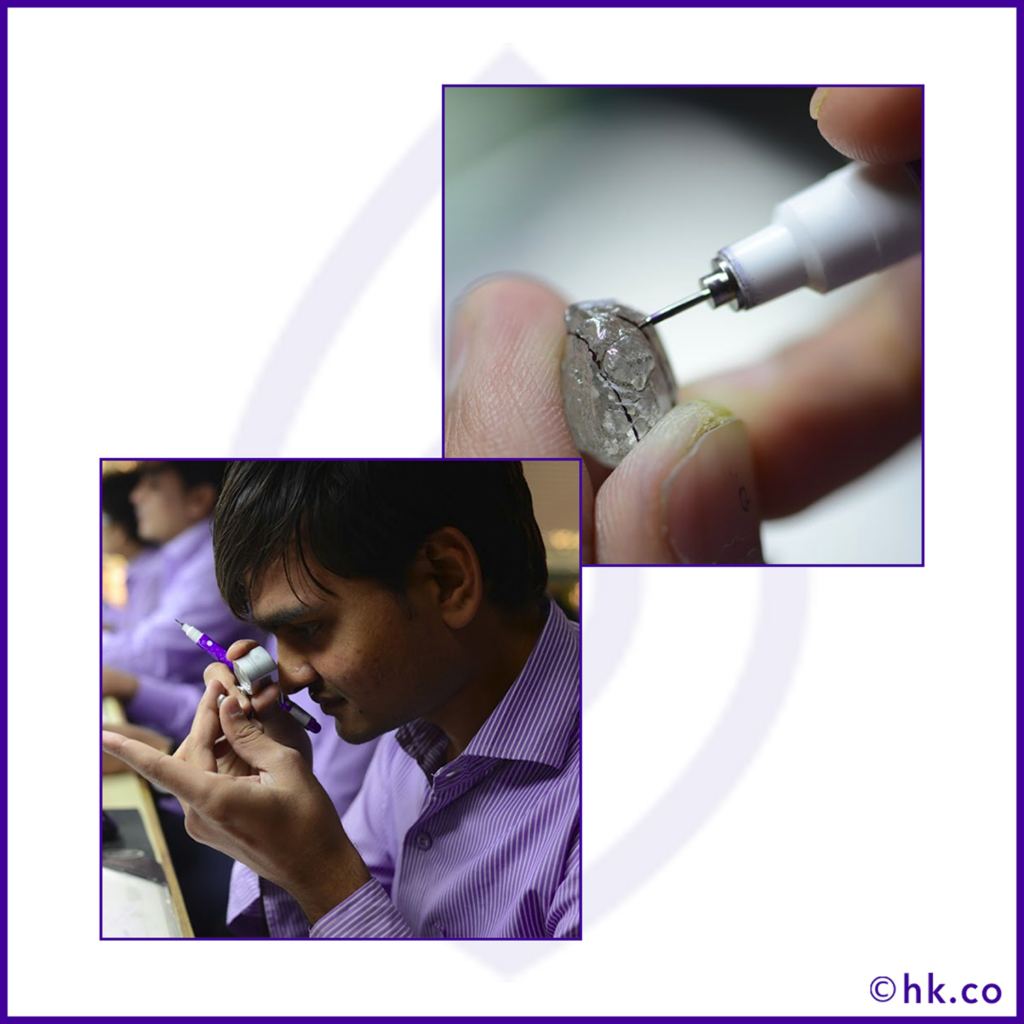

But sometimes, the experts compromise on weight retention and go for lower carat-weight to avoid any inclusions in the finished diamond and sometimes they mark slightly bigger proportions considering the possible weight loss in cutting and polishing.
In colored rough stones, the cut is critical to retain the same color in the finished diamond. Many cuts such as radiant cuts intensify the original color of the rough stone in the finished diamond.
This is the actual “cutting” part of the process where the diamond is either cleaved or sawed based on the marking done on it.
This step is to split the rough stone into separate pieces. This can be done either by cleaving or by sawing.
The basic difference between cleaving and sawing is the tool used to cut the stone. In cleaving a tool like a hammer with the blade is used and in sawing the contactless tools like lasers are used. Normally, sawing is used for cutting the oddly-shaped rough stones.
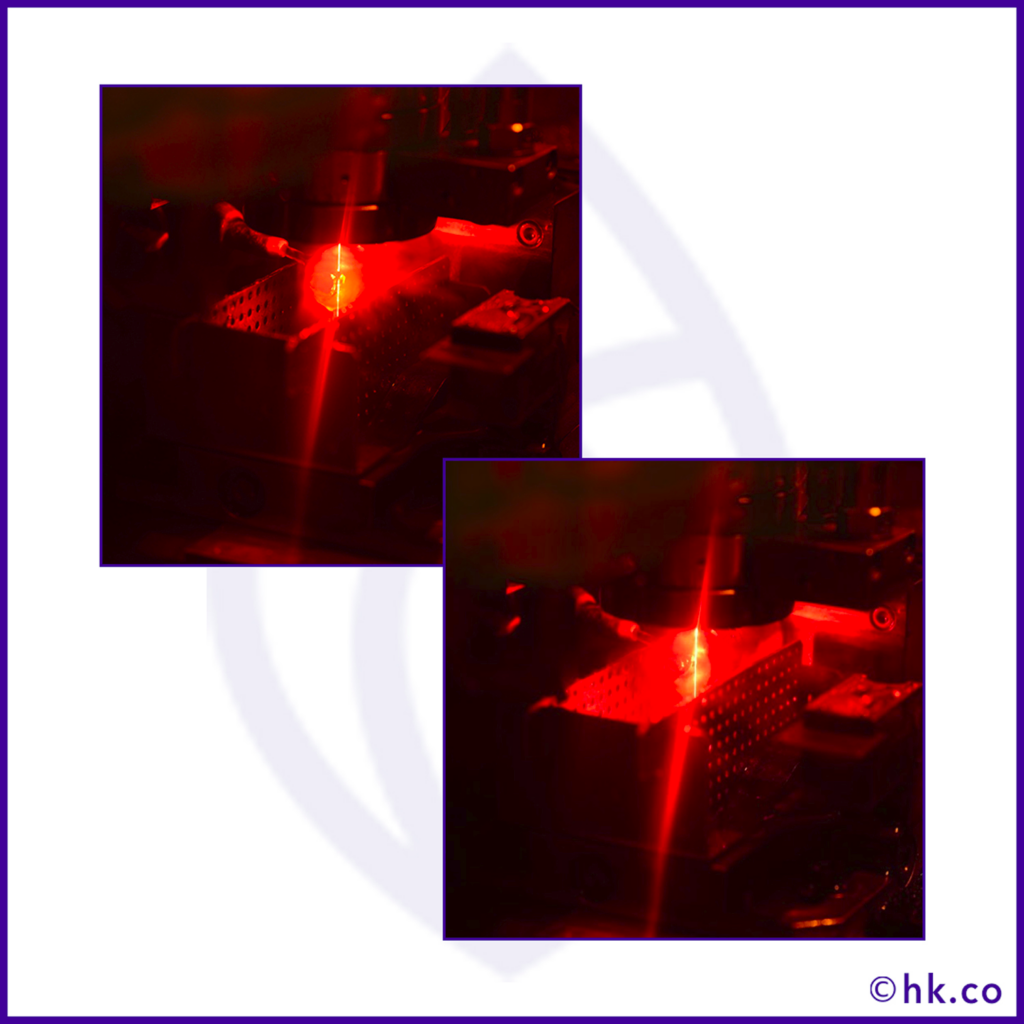
Rough stones have their weak spots aka cleavage lines that need to be carefully examined before splitting it as every stone has a distinct pattern of weak lines and the cutting angle needs to be planned accordingly.
Then the marked rough stone placed on the sawing spindle revolving at the speed of around 3000 rpm. The blade of the spindle is made of copper and layered with a mixture of oil and diamond powder.
The rough stone is then lowered to the blade and gently being tapped on the marked lines and split into the parts with the help of diamond powder, not the copper blade (since only diamond can cut a diamond)
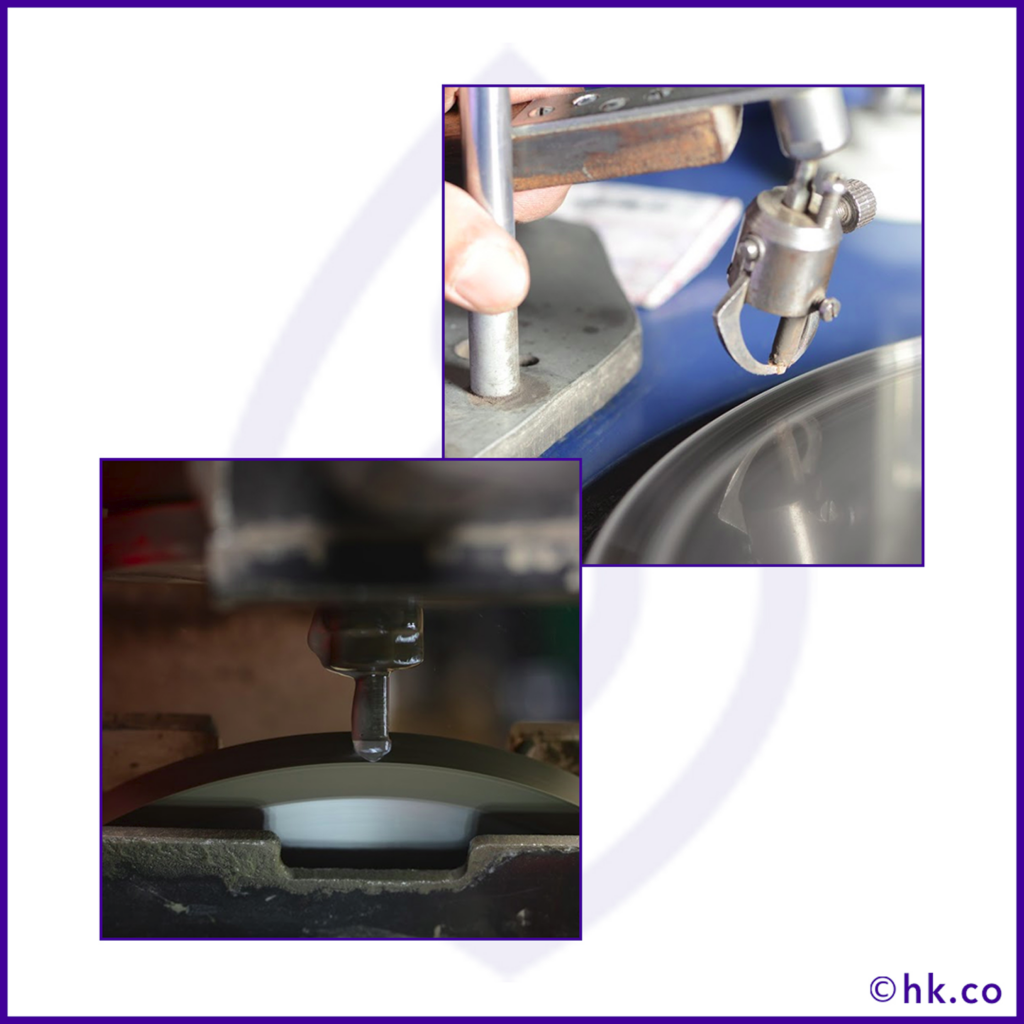
This process is more like refining the cut which has just been made.The cleaving and sawing cuts the rough stone into the right measurements but it is not a refined cut.
Bruting is done to achieve refinement and precision in the cut that is already made on the diamond.
Bruting can be done through 3 different techniques such as bruting by lasers, rubbing the stone with other diamonds in the opposite directions, disks impregnated with diamond dust.
Bruting a diamond is an art and a science. In this process, the friction is produced in either way creating a rough grindle finish and progressively down the corners of the diamond round through abrasion.

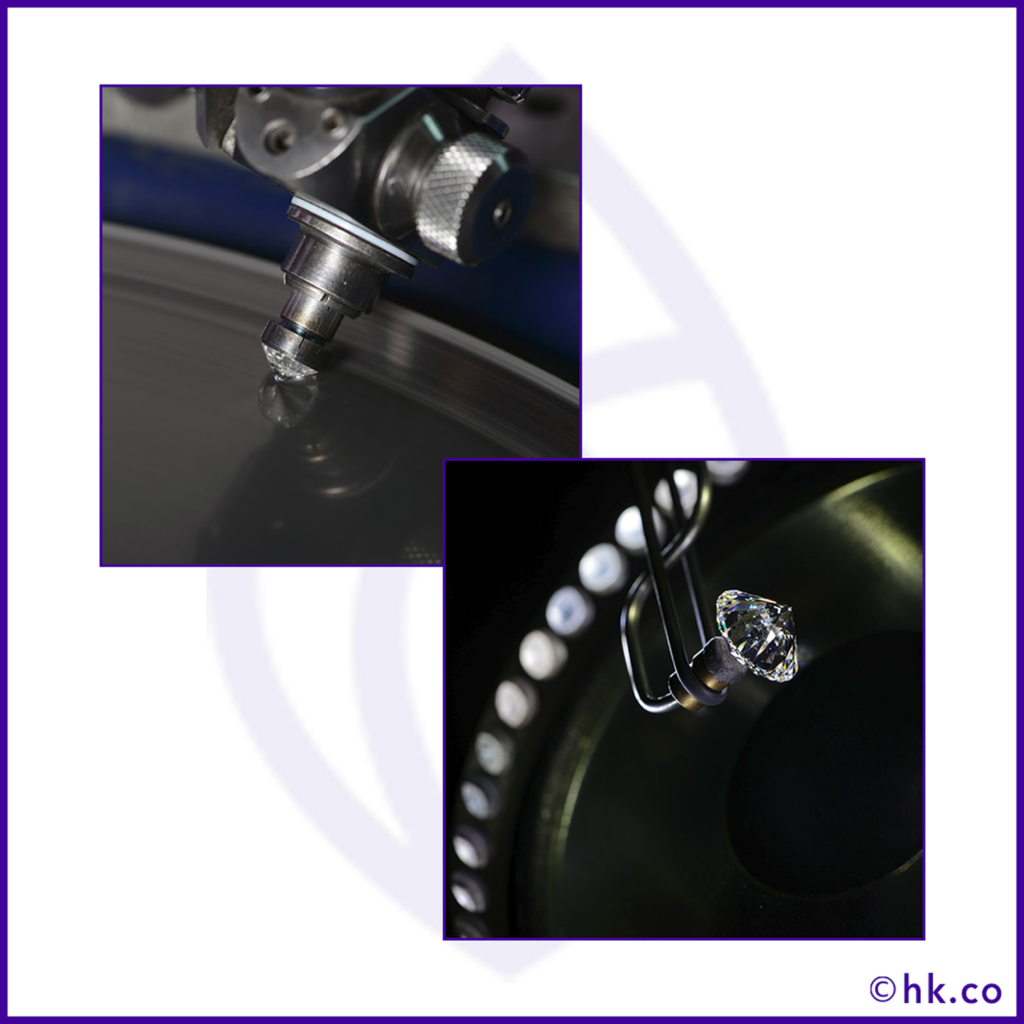
Again just like the name suggests, polishing is the step in which the diamond achieves radiance and sparkle. It also involves the forming and shaping of diamond facets. It should be done in a way that optimizes the reflection and refraction of the white light that brings sparkle and scintillation in the diamond.
Diamond polishing is done in 2 steps
In the blocking process, the main facets of the diamond including 8 pavilion, 8 crowns, 1 cutlet, and 1 table are formed; by placing a diamond into the tang and lowered on the scaife to polish the 4 main crown facets and 4 main pavilion facets.
Then these facets are further divided and polished into the rest 4 facets on the top and bottom to achieve the main 8 facets. This way the blocking makes a single cut stone template for the final/finishing stage.
In brillianteering, the final finishing of the diamond is done by adding the remaining facets of the diamond bringing a total of 58 facets (the number is subjective to the shape of the diamond).

Polishing at HK Hub
Brillianteering again requires high skills and expertise to obtain ideal proportions and perfect symmetry of the shape that ultimately determines the final aesthetics and value of the diamond.
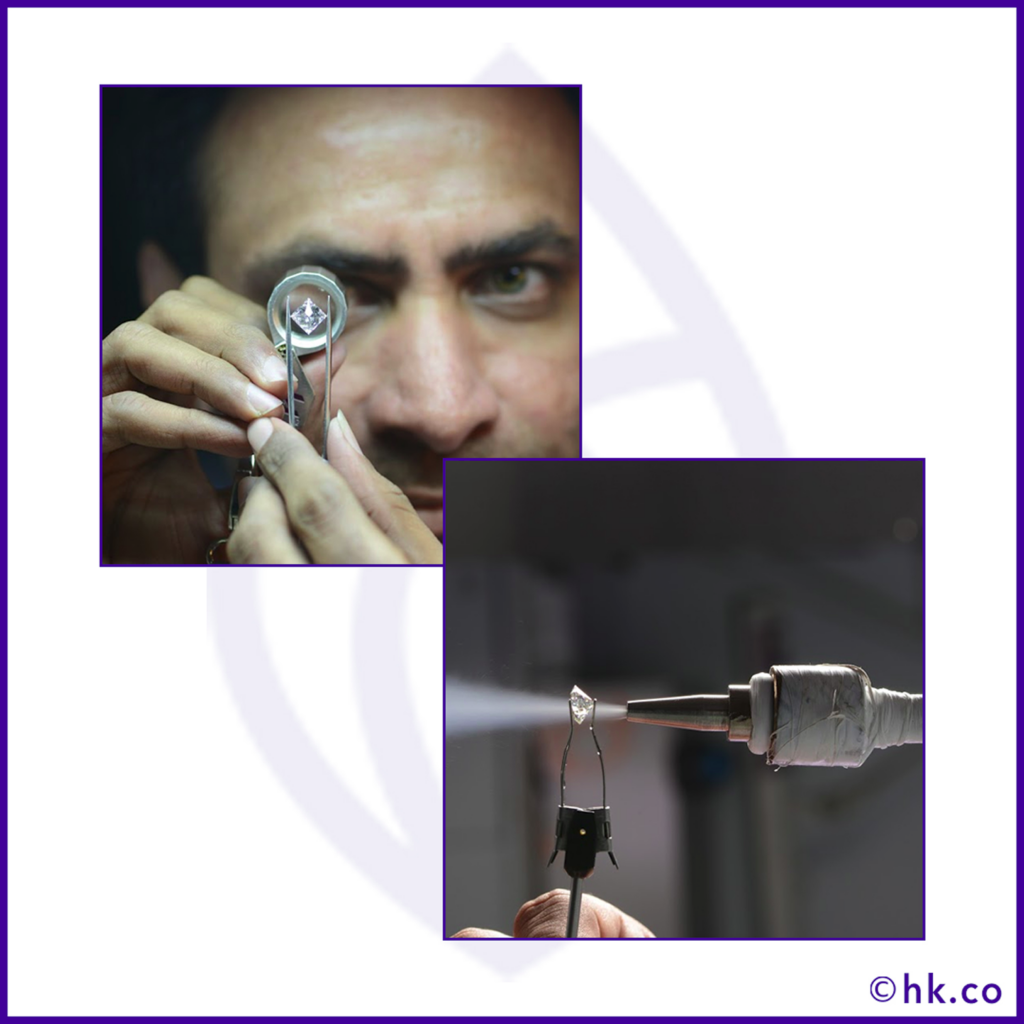
After the final polishing is done, the diamond is thoroughly cleaned with acids and goes through the final inspection process before sending it to the gemological laboratories for getting a grading certificate.
The diamond is checked to see whether it meets the quality standards such as shape, symmetry, cut, polish, etc., set by the manufacturer, and if need be, the stone would be sent back to the polishers to make improvements.

Quite frankly, it is a major determinant of the final value and price of any diamond. Since rough diamonds by themselves are not of much value. They are rough stones that need to go through a process of achieving the shape, brilliance, carat and more.
From a manufacturers perspective, it determines how much value they are able to retain throughout the cutting process to be able to sell it at a good price.
Gemological labs like GIA that examine the diamond simply provide a credible report of the characteristics of the diamond. How well it is cut, inclusions, carat, clarity and more.
Third-party certifications don’t add or subtract value from a diamond and it is in fact the cutting process that does it.
If you are seeking a positive report from GIA and other labs, simply ensure the diamond cutting process is right and that the diamonds are responsibly sourced This later reflects on the price of the diamond and the end-customer gets value for money and the sentimental value attached to such natural, beautifully cut diamonds is invaluable.
Note: The report named – ‘The Modern Diamond Cutting and Polishing’ published by GIA was taken as a reference while writing this blog
With over 30 years of experience as the leading diamond manufacturers in India, Hari Krishna Exports has set benchmarks in the industry for the art that is diamond cutting.
State of the art infrastructure and technology used by diamond experts who are passionate about the craftsmanship of natural diamonds, we produce only the best quality wholesale and loose diamonds.
Every diamond we sell comes with an in-house Faith certification along with third-party certifications from reputed geological labs like GIA, IGI, HRD, GSI, GSL, and NGTC upon request.
HK diamonds are exported to over 80+ countries, including Australia, Belgium, Europe, UAE, the USA and more.
Explore our exclusive collection of well-cut and sparkling diamonds, by registering yourself on hk.co or downloading our hk.co app available on multiple platforms including Android and iOS.